This guide will explain how to calculate a cross product in Excel.
The cross product is a mathematical operation between two vectors, a and b, that creates a new vector perpendicular to both a and b.
The cross product is signified by a cross sign “x” between two vectors. The result of a×b is defined as a vector c that is orthogonal to both a and b. Orthogonal is a mathematical term that is associated with right angles.
The new vector will have a magnitude equal to the area of the parallelogram that the vectors span.
We may also interpret the vector cross product as three separate values. These three-dimensional vector components ( i, j, and k) are all perpendicular to each other.
The cross product can be expressed in matrix notation as follows:
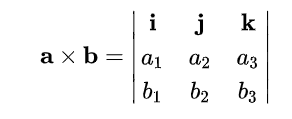
We can use Sarrus’s rule to expand the result to the following equation:

Given two vectors, a and b, in Excel, we can create a table that lists each coefficient. We’ll construct three different formulas to compute each component of the resulting vector.
The cross product of the two vectors is equivalent to the values returned by these three formulas.
Now that we know when to calculate the cross product in Excel, let’s learn how to use it and work on an actual sample spreadsheet.
A Real Example of Calculating the Cross Product in Excel
The following section provides several examples of how to use this function. We will also detail the formulas and tools used in these examples.
First, let’s take a closer look at our two vectors. Our two vectors below are written as arrays. Before we can find the cross product of these two vectors, we will have to separate each component into multiple cells.

Once we have a table of each vector component, we can follow the cross product formula to determine the components of the final vector.

Do you want to take a closer look at our examples? You can make your own copy of the spreadsheet above using the link attached below.
Use our sample spreadsheet to take a closer look at the formula of each component. You can see how the cross product changes by modifying any of the vector components.
If you’re ready to calculate cross products in Excel, head over to the next section to read our step-by-step breakdown on how to do it!
How to Calculate a Cross Product in Excel
This section will guide you through each step needed to start calculating the cross product in Excel.
Follow these steps to learn how to find the cross product of two vectors in Excel:
- First, create a table that separates the components of each vector. In this example, the components of vectors a and b are labeled ‘i’, ‘j’, and ‘k’.

- Next, we’ll add the cross product formula of each component to our spreadsheet. The algebraic notation will serve as a guide for creating the actual Excel formulas.

- We can interpret the subscript as the column number. For example, a2 can be replaced by cell D7 since it refers to the 2nd column in the ‘a’ row. This means that we can convert ‘a2b3’ to
D7*E8in our formula.

- Use the same method in the previous step to create the subtrahend.
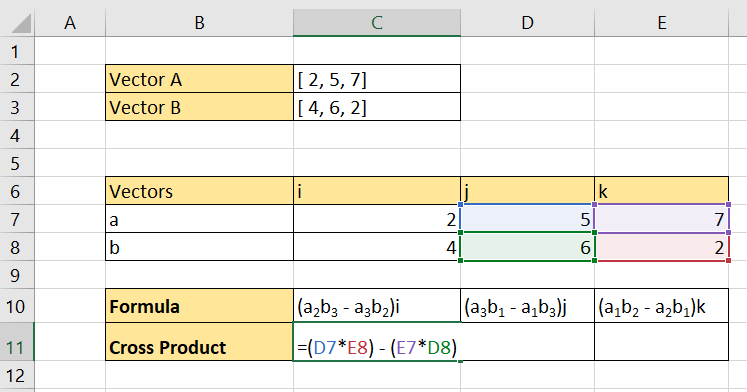
- Hit the Enter key to evaluate the formula.
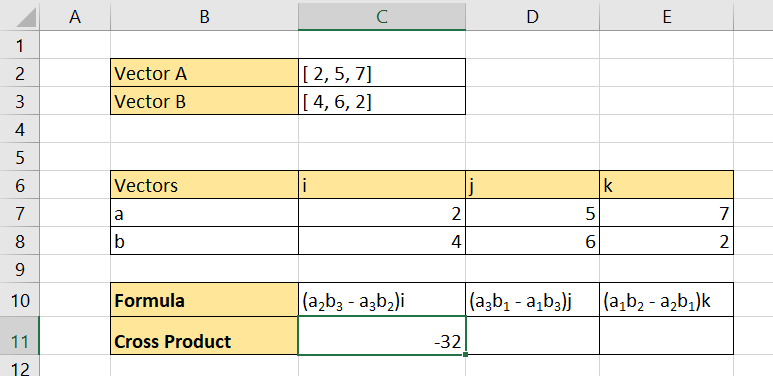
- Convert the algebraic formula of the second component into an Excel formula that references the created table.

- Next, convert the cross product algebraic formula of the third component.
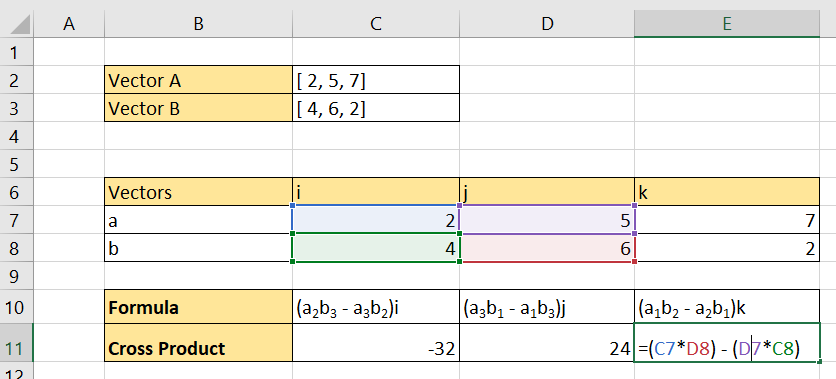
- The final cross product vector is equivalent to the three values returned by our formulas.

These are all the steps needed to do calculate the cross product in Excel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Where can we apply the cross product?
The vector cross product is a mathematical concept that has a diverse range of applications. Fields that rely on vector forces or three-dimensional interactions, such as engineering, physics, and computer programming, can use the cross product to determine what happens when two different forces interact.
The cross product operation is also used in computational geometry to define the distance between two skew lines. The operation can also determine if two vectors are coplanar. - What is the difference between dot product and cross product?
The dot product is a scalar quantity. This means that the result has a specific magnitude but no particular direction. The cross product produces a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
This step-by-step guide should provide you with all the information you need to start calculating the cross product in Excel.
Determining the cross product is just one example of the many Excel functions you can use in your spreadsheets. Our website offers hundreds of other functions and methods to help you get more out of Microsoft Excel.
With so many other Excel functions available, you can find one appropriate for your use case.
Don’t miss out on our team’s new spreadsheet tips, tricks, and best practices. Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated on the latest guides from us!







