This guide will explain how to use the AVERAGEIF function with multiple ranges in Excel.
We will present two alternative solutions to work around the limitations of the AVERAGEIF function when dealing with data spread across two or more cell ranges.
Excel’s built-in AVERAGEIF function is useful when you need to find the average of a range based on certain criteria.
For example, given a sample population, we can use the AVERAGEIF function to find the average age of people whose first name is “John” and compare it with the average age of people named “Noah”.
However, the AVERAGEIF function only works with a single range. If we have multiple ranges, we must find a workaround to use the AVERAGEIF function.
One method we can try is using the SUMIF and COUNTIF functions to calculate the sum and count of each range. After getting the sum and count of each range, we can total each sum and divide that total by the sum of each count.
A downside to this method is that the user must manually type out the ranges. The formula may also be tedious to set up when handling more than two ranges.
Another method we can try is creating a new table containing data from each range. Users can choose to create this table manually or through a built-in function like VSTACK.
After creating the table, you can now use the AVERAGEIF function normally to get the result.
Now that we know when to use the AVERAGEIF function, let’s learn how to use it and work on an actual sample spreadsheet.
A Real Example of Using AVERAGEIF with Multiple Ranges in Excel
The following section provides several examples of how to find the average of multiple cell ranges based on certain criteria. We will also explain the formulas and tools used in these examples.
First, let’s take a look at our sample dataset. We have two tables in our spreadsheet that shows daily sales of T-shirts. The T-shirt sales are broken down by color.
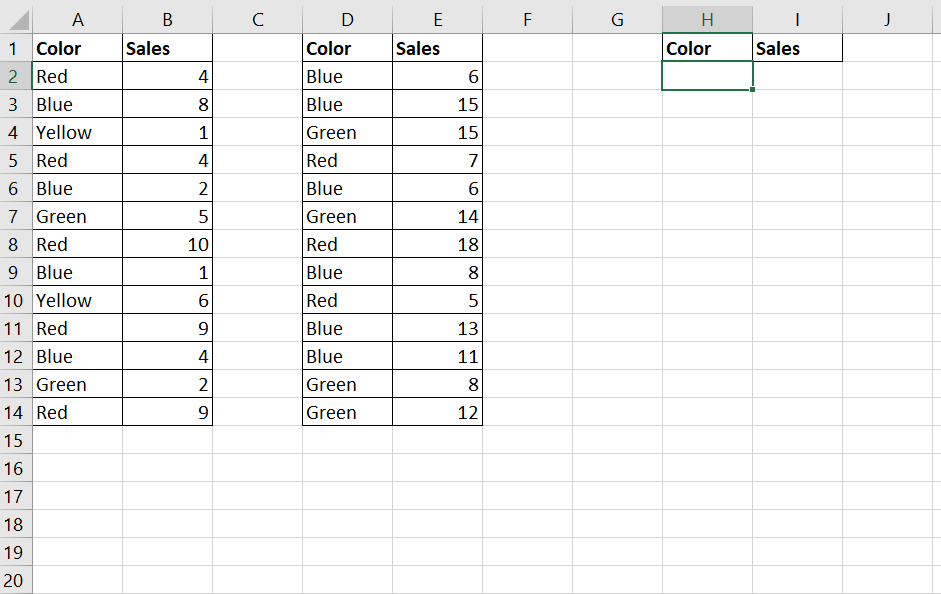
We want to find the average daily sales of red T-shirts.
Since the AVERAGEIF function only works for a single range, we will have to find a workaround.
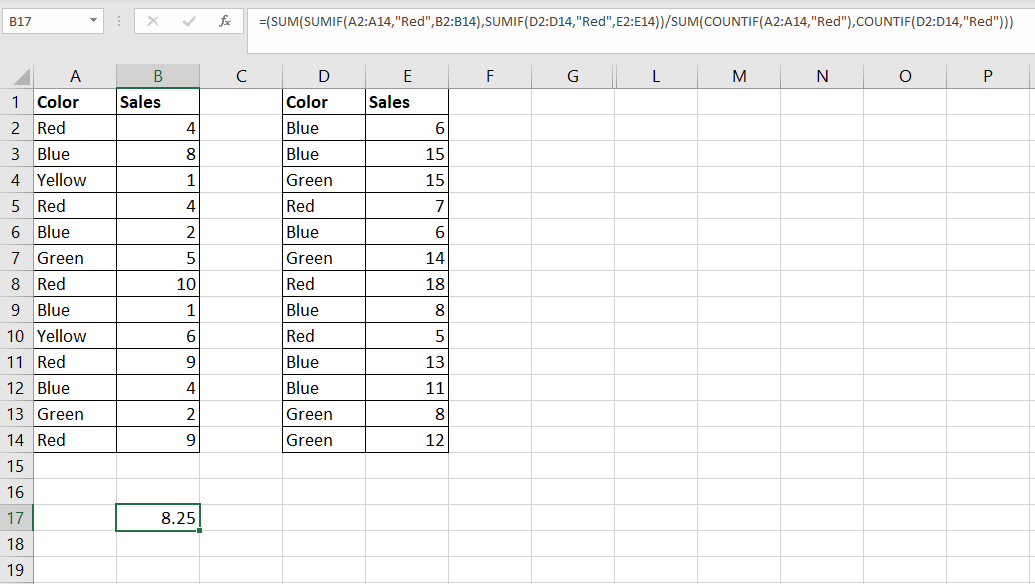
In the example above, we used a combination of SUM, SUMIF, and COUNTIF functions to create a formula that behaves similarly to the AVERAGEIF function.
To get the value in cell B17, we just need to use the following formula:
=(SUM(SUMIF(A2:A14,"Red",B2:B14),SUMIF(D2:D14,"Red",E2:E14))/SUM(COUNTIF(A2:A14,"Red"),COUNTIF(D2:D14,"Red")))
Another way we can use the AVERAGEIF function is by combining both ranges into a single continuous range.

To add both ranges together, we can use the following formula:
=VSTACK(A2:B14, D2:E14)
Do you want to take a closer look at our examples? You can make your own copy of the spreadsheet above using the link attached below.
If you’re ready to try out these methods, head over to the next section to read our step-by-step breakdown on how to do it!
How To Use AVERAGEIF With Multiple Ranges In Excel
This section will guide you through each step needed to start using the AVERAGEIF function with multiple ranges in Excel. You’ll learn how we can
Follow these steps to start using the AVERAGEIF function with multiple ranges in Excel:
- First, select an empty cell that will hold the output of our
VSTACKformula. TheVSTACKfunction allows us to create a new table that combines two or more ranges into a single continuous range that we can use for theAVERAGEIFformula.
 In this example, we want to combine the cell ranges A2:B14 and D2:E14.
In this example, we want to combine the cell ranges A2:B14 and D2:E14. - Type the formula ‘=VSTACK(‘ to start the
VSTACKfunction in Excel.

- The
VSTACKfunction accepts 1 or more arguments. For the first argument, enter the first range you want to combine.
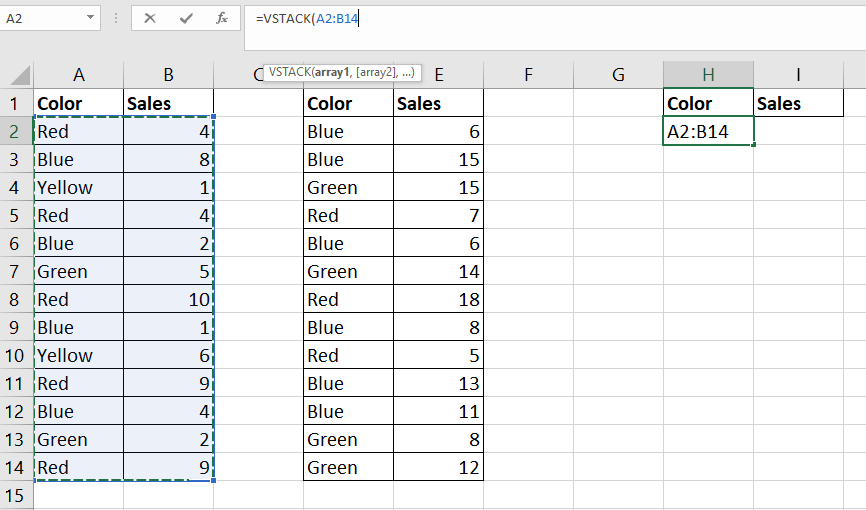
- Proceed to add each additional range as a new argument for the
VSTACKformula.

- Hit the Enter key to evaluate the
VSTACKfunction.
 The output of the
The output of the VSTACKformula is dynamic. Changes made to the original ranges will reflect in the output. - Now that we’ve combined the separated ranges, we can proceed with the
AVERAGEIFfunction.
Click on an empty cell and type ‘=AVERAGEIF(‘ to start theAVERAGEIFfunction.

- Enter the range that will be compared against the criteria.
 In this example, we’ve selected the color field as our range to check.
In this example, we’ve selected the color field as our range to check. - Next, enter the criteria to use as the second argument. Add the numerical range to average as the third argument.
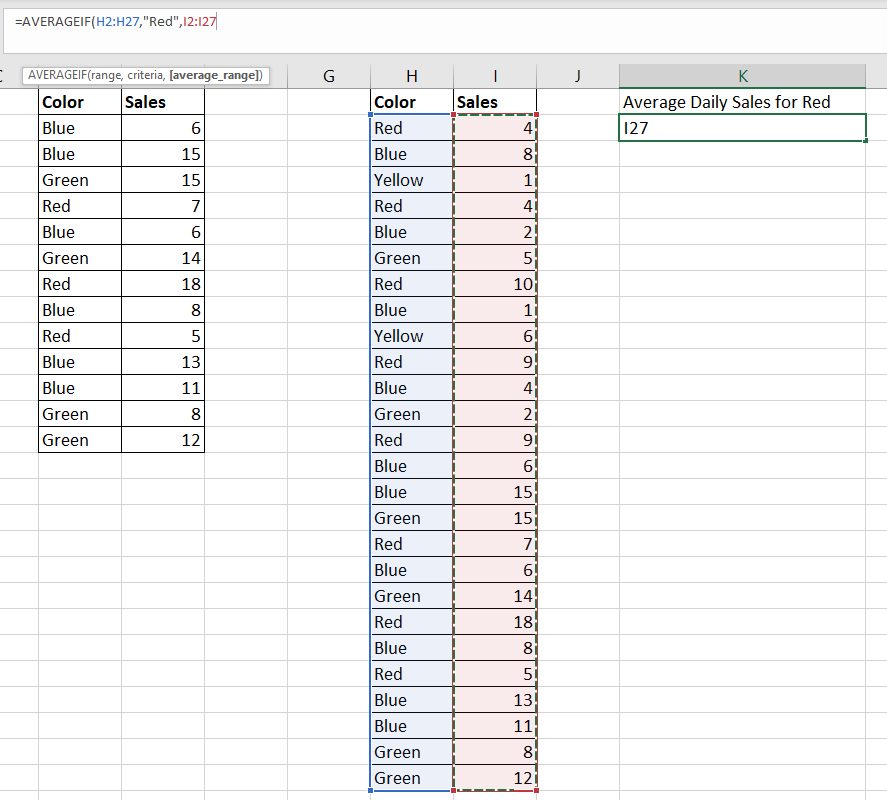 In our example, we want to only find the average of sales where the equivalent color is ‘Red’.
In our example, we want to only find the average of sales where the equivalent color is ‘Red’. - Hit the Enter key to evaluate the formula.
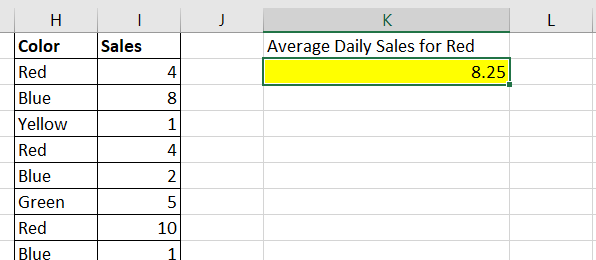 In our example above, we’ve determined that the average daily sales for red T-shirts is 8.25.
In our example above, we’ve determined that the average daily sales for red T-shirts is 8.25. - If you want to avoid creating a new table, we can use a combination of
SUM,SUMIF, andCOUNTIFfunctions to find the average given a condition.
 In the example above, we’ve obtained the same result without having to create a new table or use the
In the example above, we’ve obtained the same result without having to create a new table or use the AVERAGEIFfunction.
These are all the steps needed to find the average of multiple ranges based on a certain condition.
This step-by-step guide should provide you with all the information you need to start using the AVERAGEIF function with multiple ranges in Excel.
We’ve shown you how to use the VSTACK function to combine multiple ranges into a single range. We’ve also provided an alternative formula that simulates the AVERAGEIF function using the SUM, SUMIF, and COUNTIF functions.
The AVERAGEIF function is just one example of the many Excel functions you can use in your spreadsheets. Our website offers hundreds of other functions and methods to help you get more out of Microsoft Excel.
With so many other Excel functions available, you can find one appropriate for your use case.
Don’t miss out on our team’s new spreadsheet tips, tricks, and best practices. Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated on the latest guides from us!







